When you stripe (RAID 0) two mirrored arrays (RAID 1) arrays you produce a RAID 10. This quick guide offers a simplified explanation of RAID 10, its benefits and shortcomings.
What is RAID 10 (RAID 1 + RAID 0)?
As I pointed out in the introduction, RAID 10 is striping two mirrored volumes. To understand the benefits and shortcomings of RAID 10, it is important to understand disk striping without parity (RAID 0) and disk mirroring (RAID 1).
For a simplified understanding of these RAID levels, click RAID 50 vs RAID 10: Benefits and Disadvantages Compared.
Benefits and Shortcomings of RAID 10
Before I summarize the benefits and shortcomings of raid 10, I will list the benefits and shortcomings of RAID 1 and then RAID 0.
Benefits and Shortcomings of RAID 1
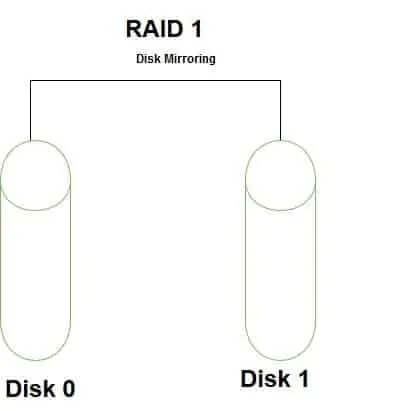
Below are the advantages of RAID 1
- Excellent Read and Write Speed: RAID 1 delivers improved Read. When data is Read, it is read from one disk, making Read fast.
- Provides Data Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: Because data is written to two disks, if one of the disk fails, you can easily recover the array. However, when you replace the failed disk, the array will automatically rebuilt itself.
Here are the shortcomings of RAID 1:
- Delivers 50% of Available Disk Space: Disk mirroring requires two disks. However, the same Data is copied (mirrored) to both disks. What this means is that just half of both disks is available to store your data. The other half is kind of “wasted”. Well, it is not really “wasted” as it is used for redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Reduced Performance During Rebuild: If RAID 1 fails and requires rebuild, you will still be able to access your data. But data access will be at reduced performance.
Benefits and Shortcomings of RAID 0
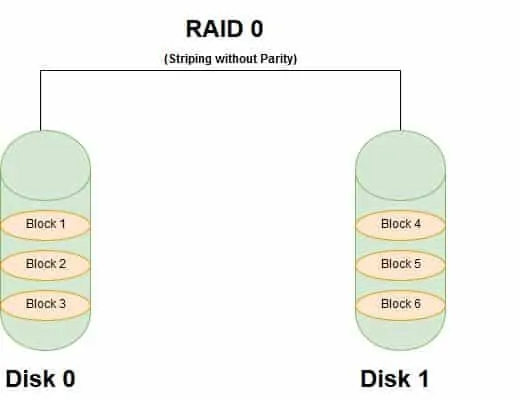
Here are the benefits of RAID 0:
- Improved Read and Write Performance: Striping without parity effectively combines two physical disks into a single volume. The resultant volume offers almost two times the performance of both disks.
- Increased storage Capacity: Unlike RAID 1 array, RAID 0 create double the size of the disks or at least double the size of the smallest disk. This comes at a cost as you will see shortly.
Below are the shortcomings of RAID 0:
- Does NOT offer Data Redundancy or Fault Tolerance: RAID 0 does not offer any form of data redundancy. Meaning, if any of the disks that form the array fails, ALL data is lost. There is no way to recover except you have a backup.
Benefits and Shortcomings of RAID 10 Summarized
RAID 10 combines the speed of RAID 0 (Disk striping) and the fault tolerance of RAID 1 (Disk mirroring). The table below summarizes the benefits and shortcomings of RAID 10:
| S/N | Feature | Benefits | Shortcomings |
| 1 | Availability of Disk Space | Only 25% of the disk is available for storage. RAID 10 requires 4 disks. But because each RAID 1 set is a mirror, they deliver 1 disk storage capacity each. | |
| 2 | Performance | RAID 10 offers improved performance (speed) as data is striped across multiple disks. | |
| 3 | Data Redundancy and Fault Tolerance | *The mirrored volumes offers redundancy and fault tolerance. | |
| 4 | Performance During Rebuild | Performance will be slightly degraded during a RAID rebuild. |
Conclusion
This quick reference guide highlighted the benefits and shortcomings of RAID 10. The benefits of RAID 10 are improved Read and Write, fault tolerance and data redundancy. shortcomings of RAID 10 are deliver 25% of the disks to use for storage and reduced performance during array rebuild.
We love to hear from you. Kindly share your thoughts or ask a question about this guide by responding to the “Was this page helpful” question below.
Alternatively, use the “Leave a Reply” form at the bottom of this page.



