Have you ever wondered what you would do if your organization’s Active Directory suddenly became corrupt or lost? Fear not, because in this article, we’ll guide you through the steps to restore Active Directory from backup.
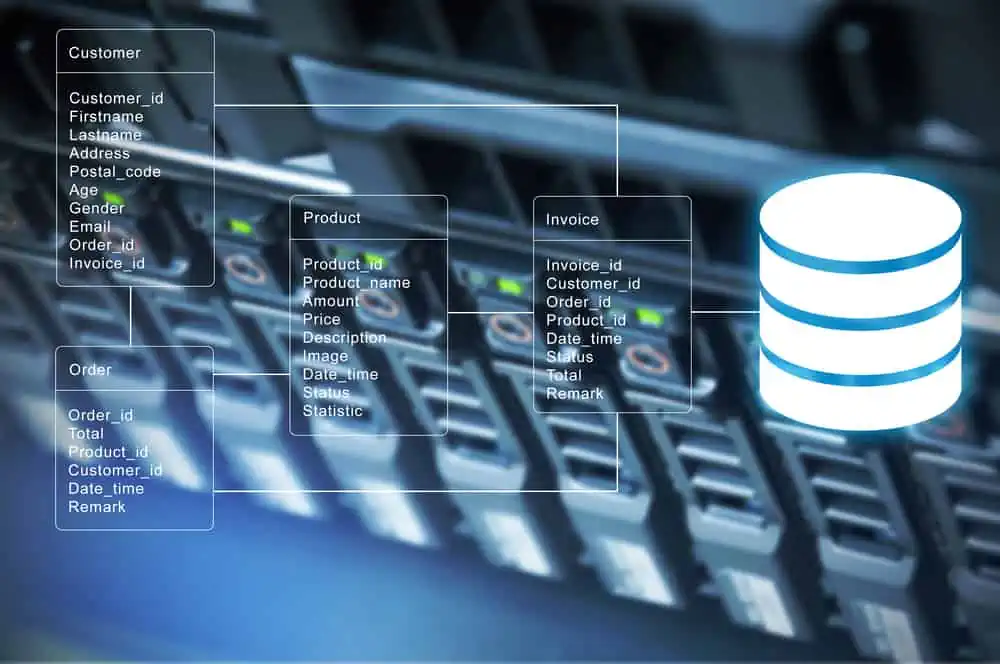
The process in this article involves restoring System state from backup. When you restore System state, which includes Active Directory from backup, your server will be restored to its state when you took the backup. This includes the Server Edition and licenses.
Step 1: Boot to Directory Services Repair Mode (DSRM)
Before you can restore Active Directory from a backup, you must first boot to Directory Services Repair Mode (DSRM). If you try to restore AD while logged in normally to Windows, you’ll receive an error message.
Follow the steps below to boot Windows Server 2019 to DSRM:
- Restart the server normally. Then, when Windows is restarting, press and hold the server’s power button until it shuts down.

- Press the power button again to start the server; when it starts booting to Windows, press and hold the power button again to shut the server down.
- When you start the server for the third time, it will boot to Recovery mode. Then, click “See advanced repair options” on the Recover screen.
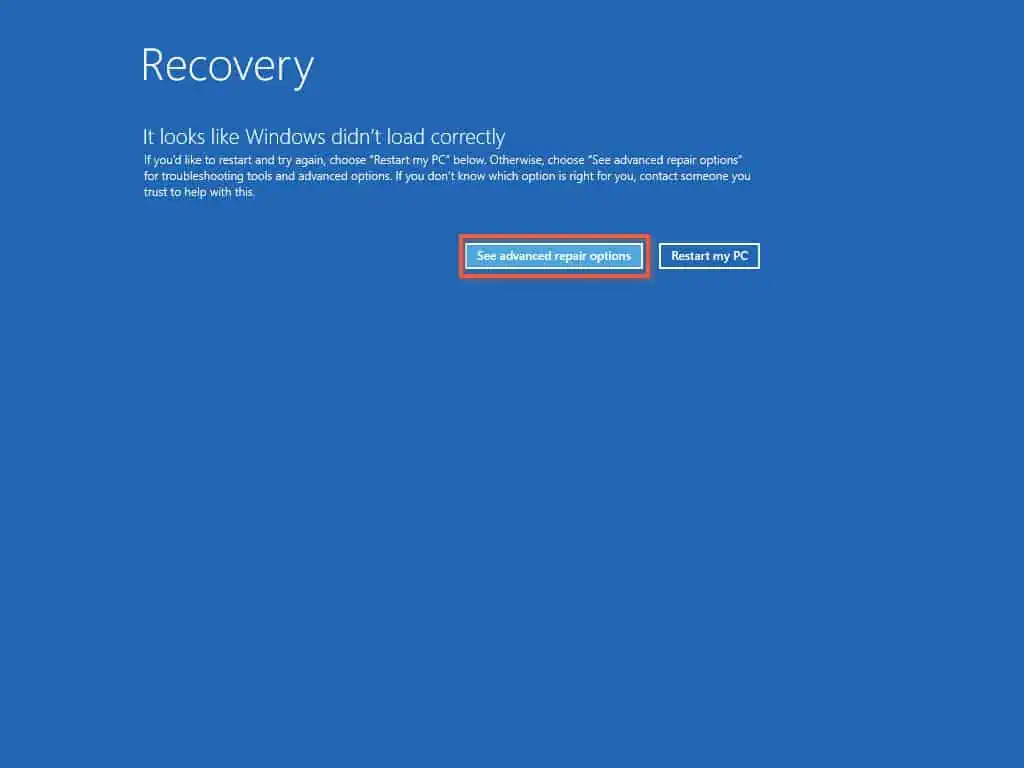
- Next, on the Choose an option page, click “Troubleshoot.”
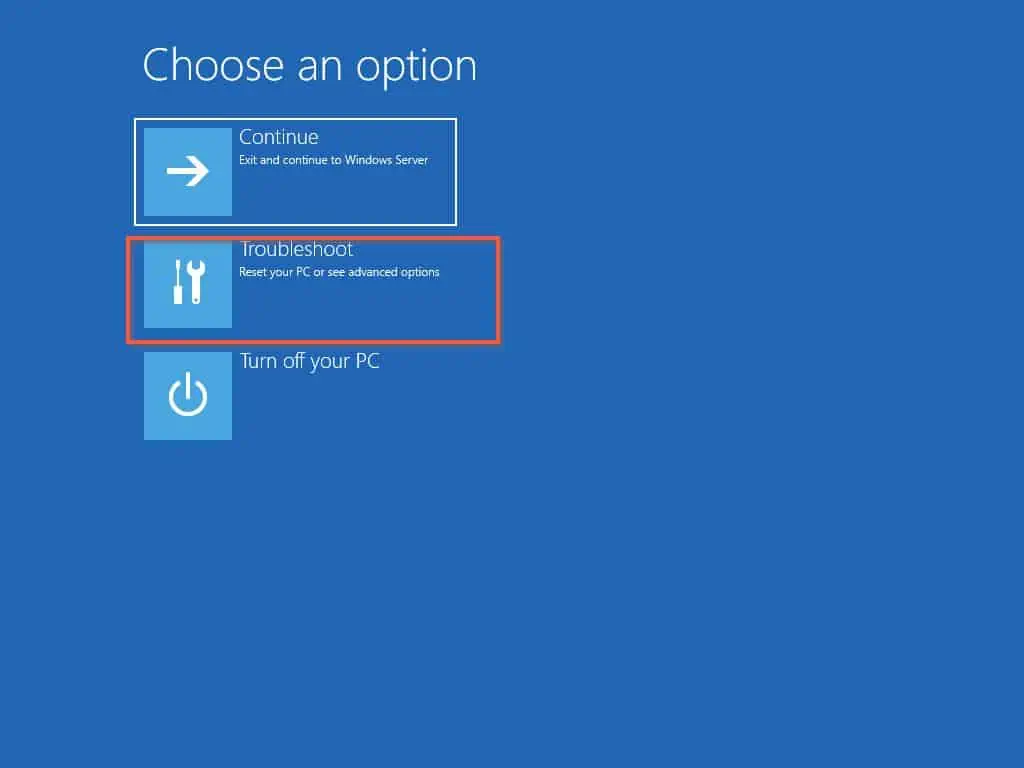
- Then, on the Advanced options page, click “Startup Settings.”
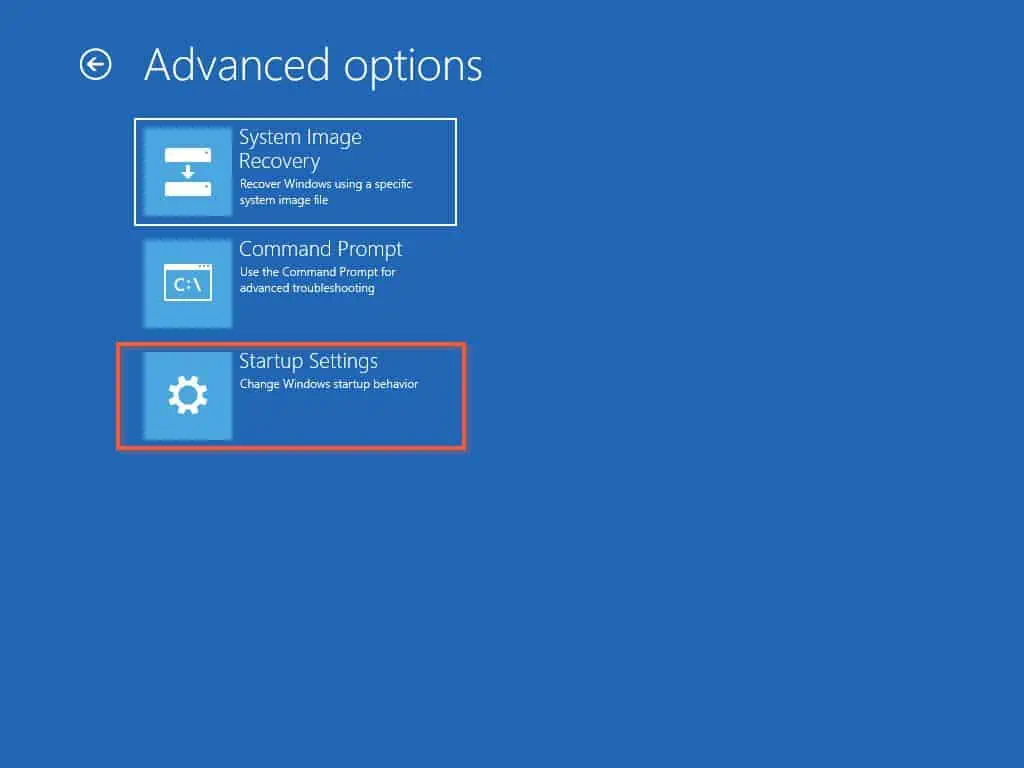
- On the Startup Settings page, click “Restart.”
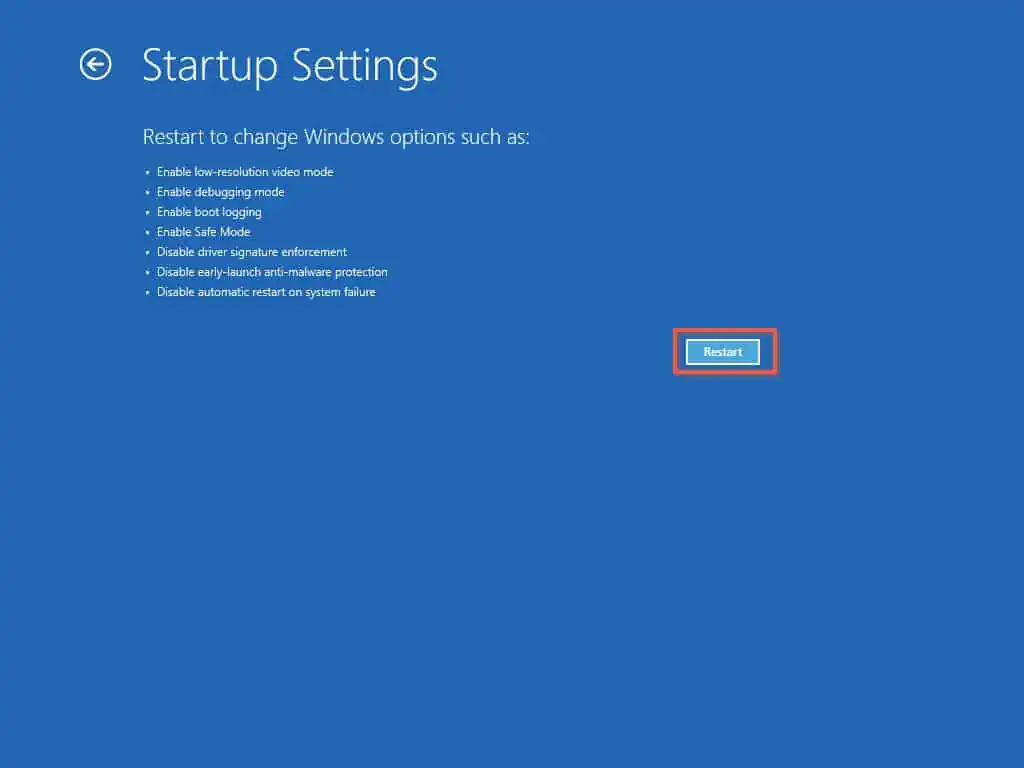
- Finally, on the Choose Advanced Options for: Windows Server page, use the Up/down arrow key on your keyboard to select “Directory Services Repair Mode,” then press the Enter key on your keyboard.
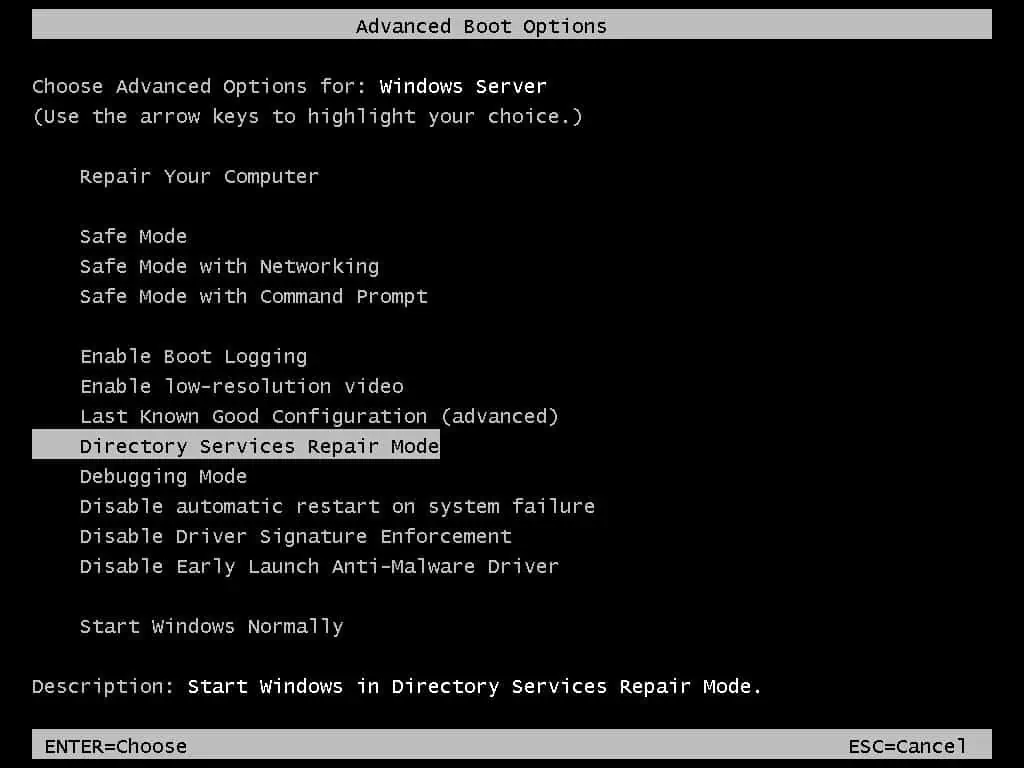
Windows will boot to the login screen. To log in, enter your user name as shown below. Replace “administrator” with your local administrator login name.
.\administrator
Once you log in successfully to restore Active Directory from backup, proceed to the second section of this guide.
Step 2: Restore Active Directory in DSRM
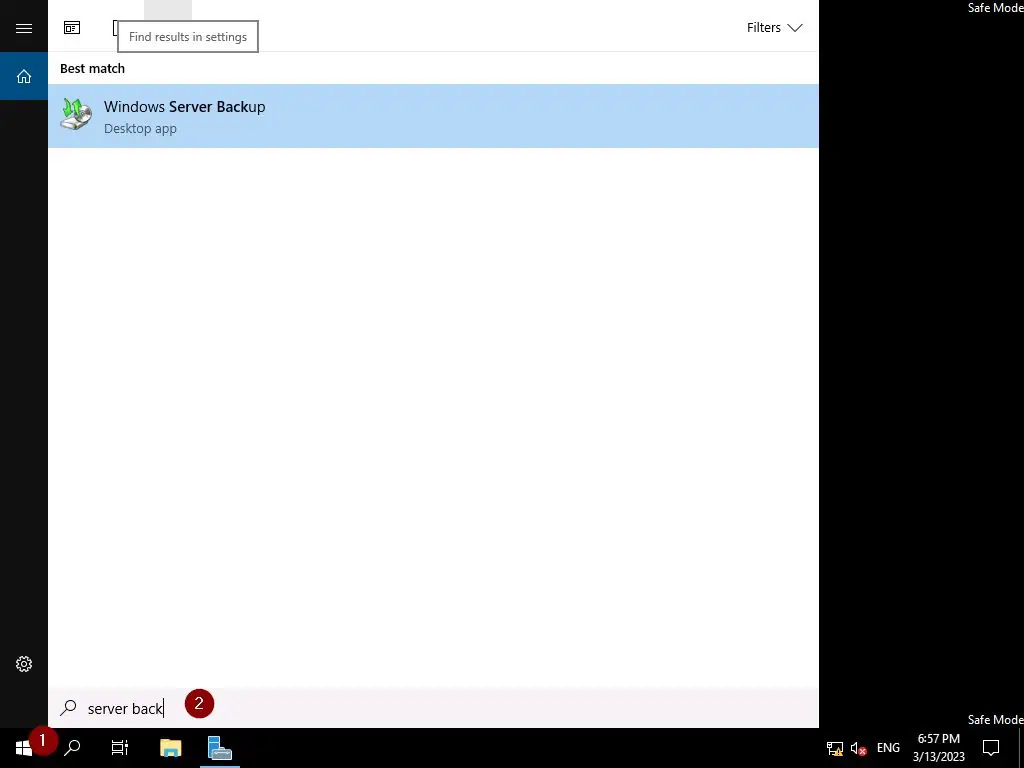
- Once you’ve logged in to the server, search for and open Windows Server Backup.
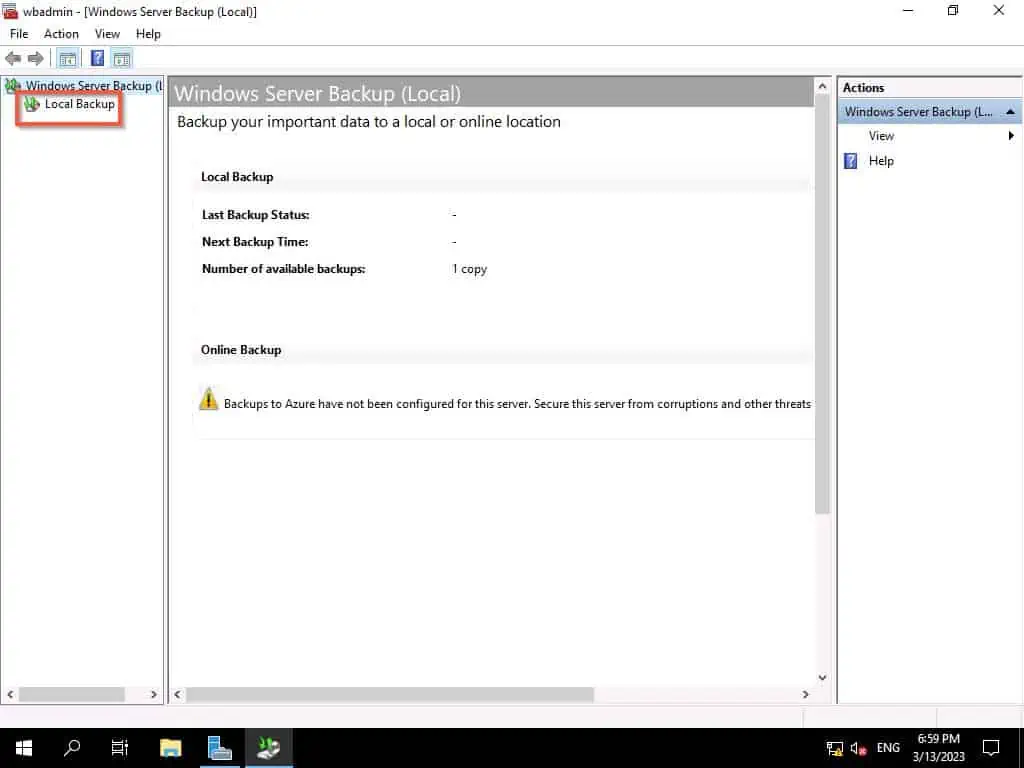
- Then, when On the Windows Server Backup window, click “Local Backup.”
- Next, wait for Windows BAckup to load the page – once it is loaded on the third pane, click Recovery.
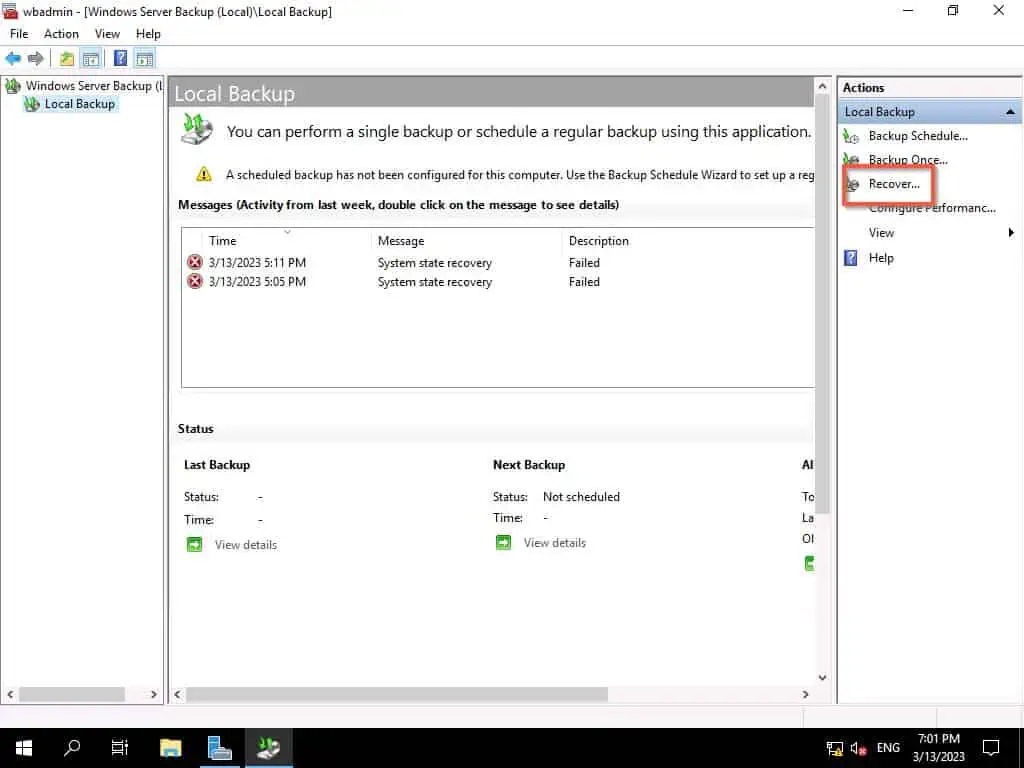
- When the first page of the Restore wizard opens, select an option, then click Next.

- Then, select the backup you wish to restore and click Next.
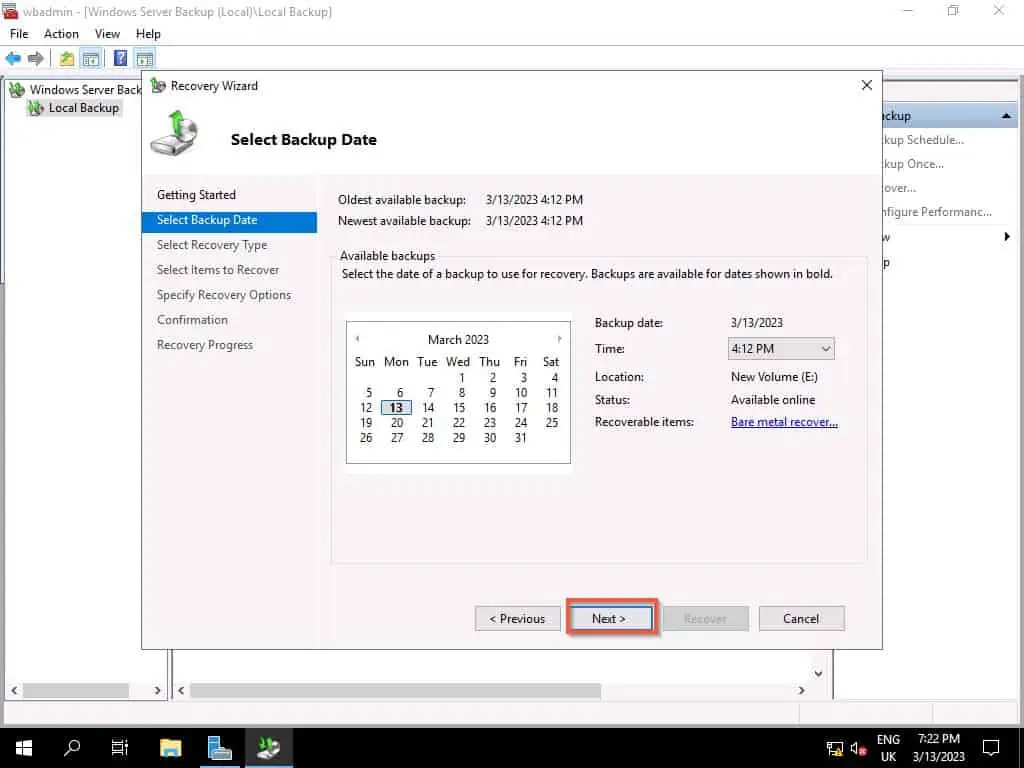
- When the Select Recovery Type page opens, select System state and click Nex.
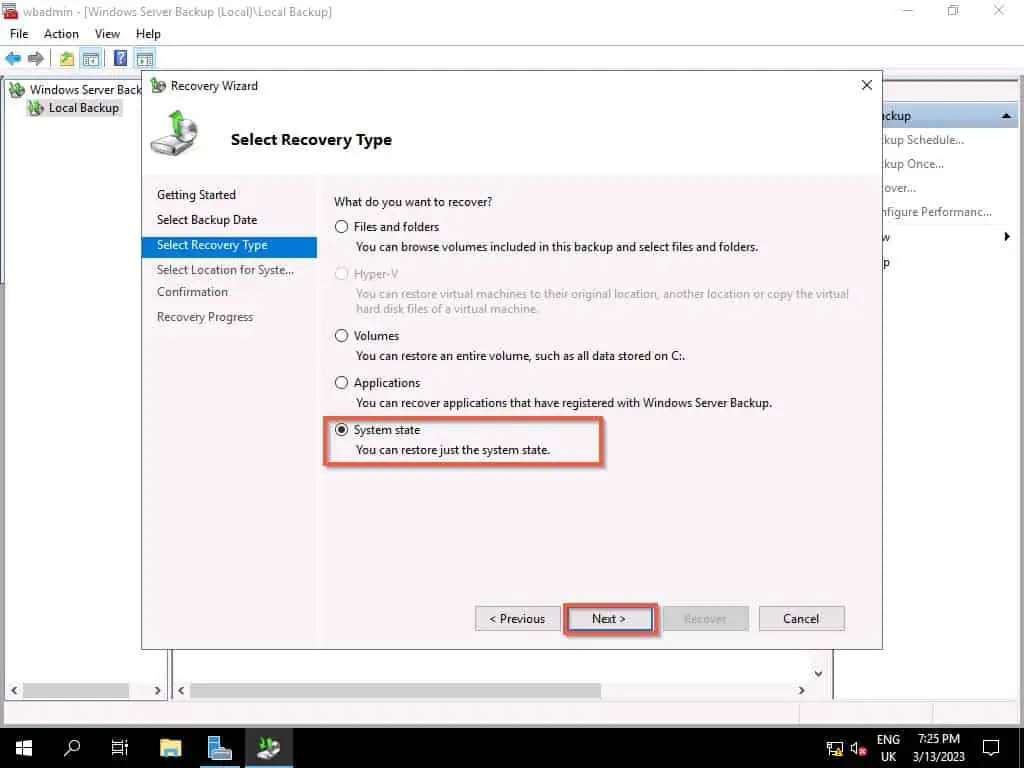
- When the Select Location for System State Recovery page, select Original Location and click Next.
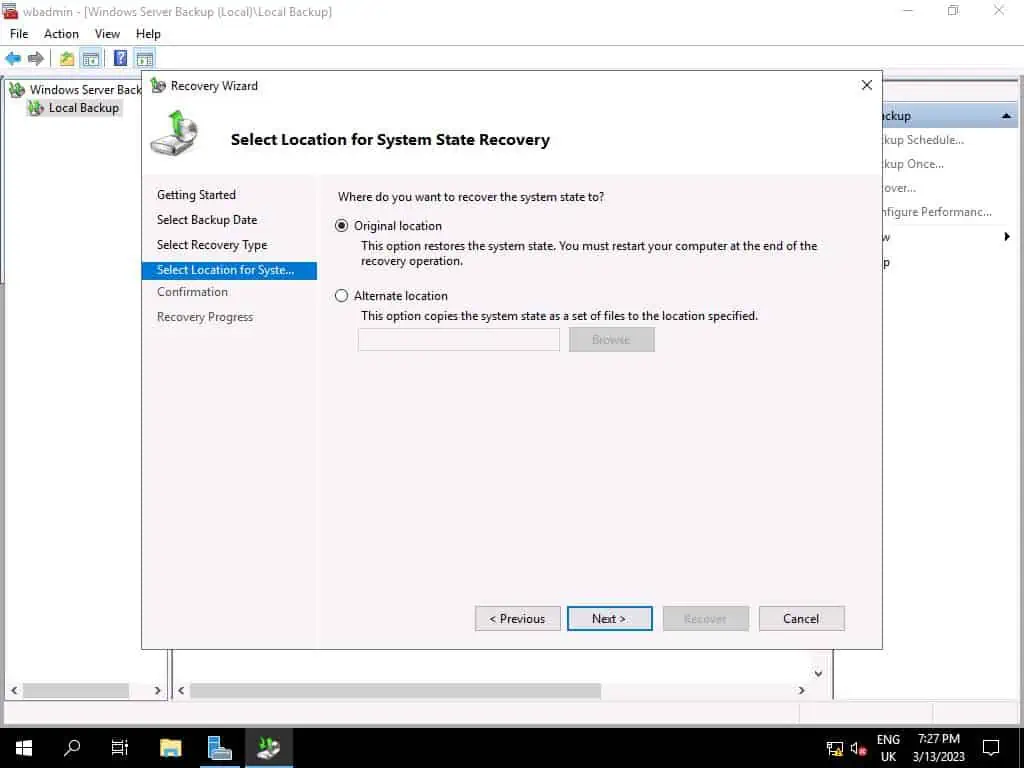
- Then, click Recover, then to confirm that you wish to continue, click Yes.
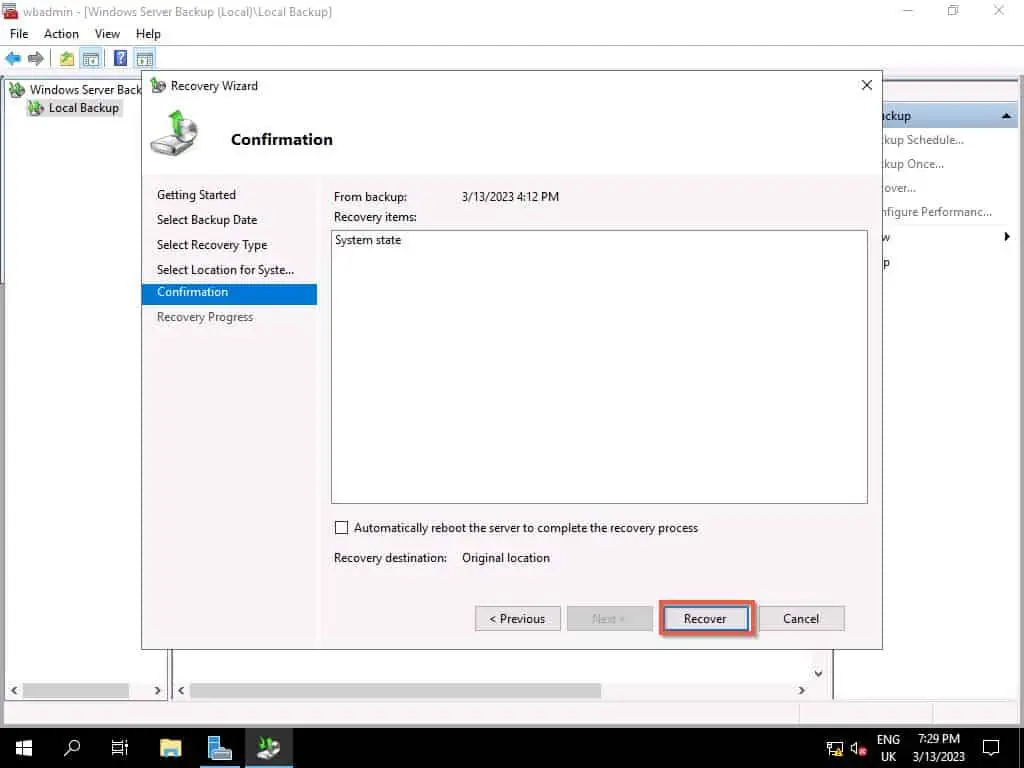
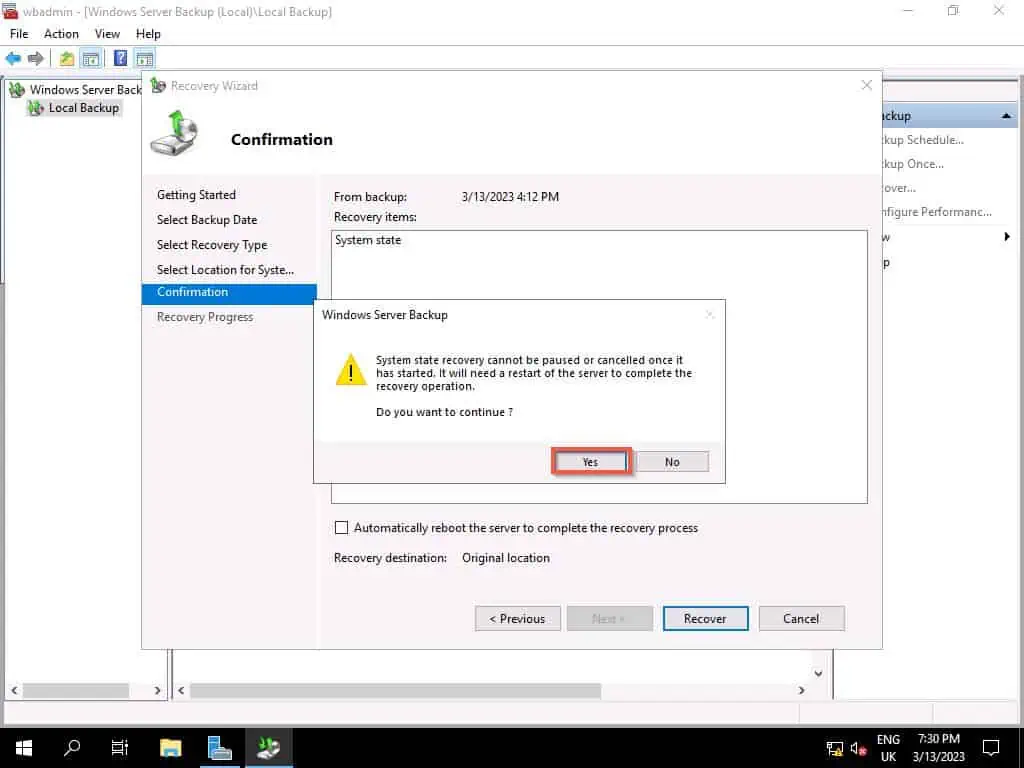
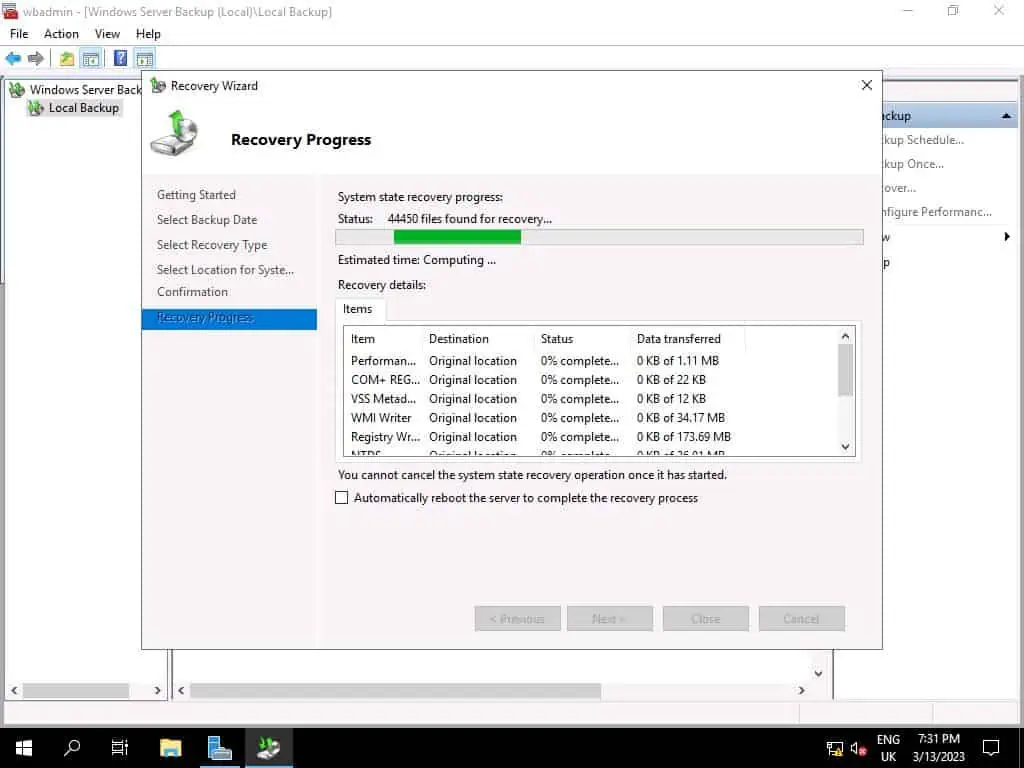
- Finally, wait for the Active Directory backup recovery to complete. Depending on the size of your AD database, this process could take a while.
When the restore completes, click Restart. When the server restarts, log in to AD as normal and test that the restore was completed successfully.
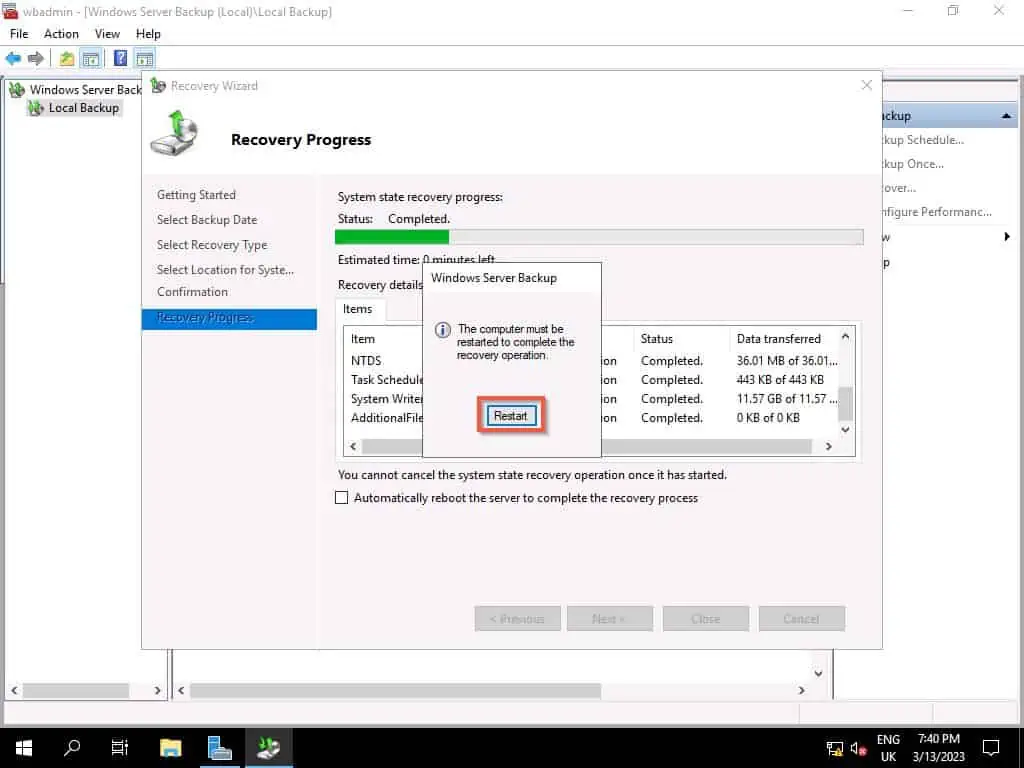
When your server restarts, your Active Directory will be restored to the state it was when you took the backup.
Frequently Asked Questions
Follow the steps below to restore AD from backup:
a) If you reinstalled Windows Server, install the AD DS role and promote the server to a Domain Controller. Otherwise, proceed to the next step if the server is already a DC.
b) Boot the Windows Server to Directory Services Repair Mode (DSRM)
c) Restore System state backup
If you backup the System state of a Domain Controller, the backup file includes Active Directory database. So, restoring the System state backup restores the Active Directory.
The Directory Services Repair Mode (DSRM) – used to be “Restore” – is the “Safe” mode boot for an AD server. When you start an Active Directory Domain Controller in DSRM, you can restore AD DS from a backup.
Deleting a computer from AD removes the computer account from the directory database. Additionally, all associated security credentials for the computer are also removed from the AD database.
The implication of this is that the deleted computer will no longer authenticate to the domain, access network resources, or receive group policy settings.
Yes, it is possible to recover a deleted object in AD. However, the recovery process depends on your configuration.
If you enabled Active Directory Recycle Bin before deleting the object, you could restore the object from Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC).
However, if you did not enable Active Directory Recycle Bin but have a recent System state backup, you can perform an Authoritative restore of the object. Performing an Authoritative restore forces Active Directory to replicate the restored object to other Domain Controllers in the domain.
It is important to mention that your ability to restore a deleted object – whether via AD Recycle Bin or restore from backup – depends on the Tombstone lifetime of your AD forest.
The Tombstone Lifetime in Active Directory (AD) is how long AD keeps deleted objects in the database before they are permanently deleted and removed. The default Tombstone Lifetime in a new AD forest is 180 days, but you can change this value using PowerShell or ADSI Edit.
Conclusion
Active Directory is a multi-master directory database. This means that all domain controllers have an exact replica of the database.
This implies that you would rarely need to restore Active Directory from backup. However, if AD gets corrupted or becomes inoperable in the rate instance, you may resort to restoring AD from a backup.
If you found yourself in this rare situation, I am confident that you would have been able to restore your AD from a backup using the steps in this article. If you did, click on “Yes” beside the “Was this page helpful” question below.
You may also express your thoughts and opinions by using the “Leave a Reply” form at the bottom of this page.
Finally, visit our Active Directory Guides page for more Active Directory articles.



