Is the Disk in Windows Task Manager the same as the actual disk usage on a computer? This guide on “disk in task manager” answers this question.
Overview
Every Windows Operating system has a task manager that you can access.
To access the Windows Task Manager, press the Ctrl + Alt + Del keys together and select “Task Manager.” You can also press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on the keyboard to open the Task Manager straight from the desktop.
One of the tabs on the Task Manager window is the “Processes” tab. The Processes tab has several information columns, including the ” Disk ” column.
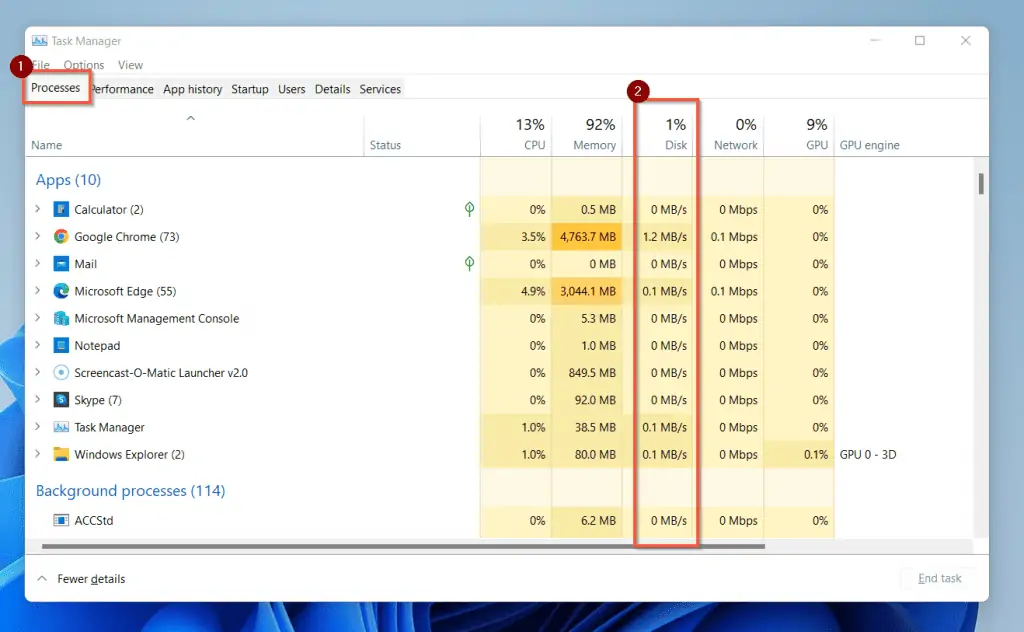
Like other columns in the processes tab, the disk column has values in MB/s for every running application. Above the Disk header, another percentage value (1% in my screenshot above) shows the disk utilization by running processes.
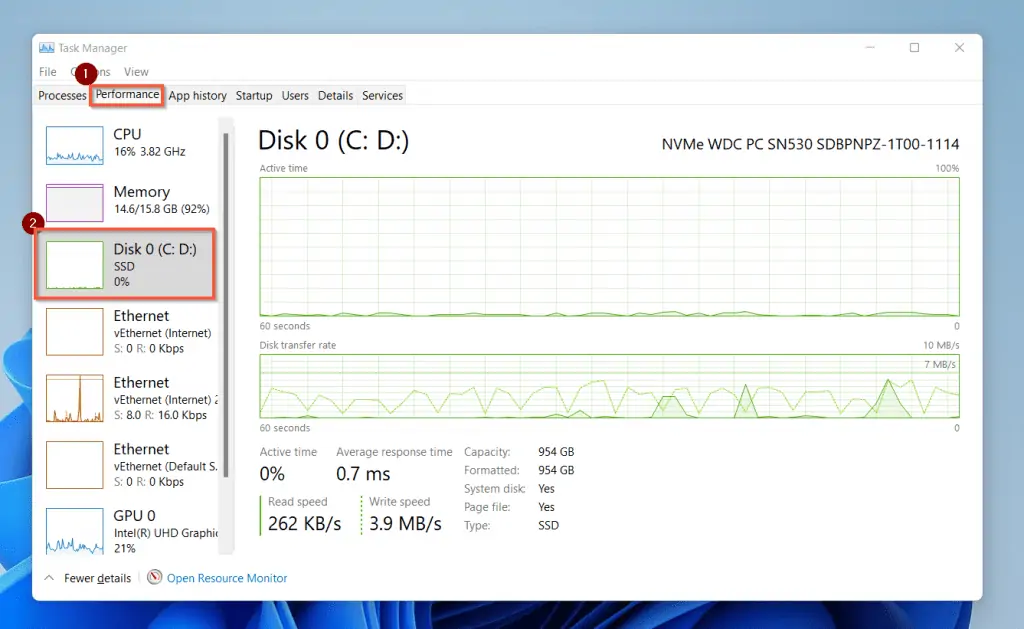
Moreover, you can view a graphical presentation of the disk usage by switching to the “Performance” tab and clicking on “Disk.” The performance tab simulates the disk usage graphically.
In effect, disk in task manager indicates the disk’s capacity currently being used (disk utilization) by your computer to run programs. Therefore, it relates more to the performance of your hard disk rather than its storage capacity.
How Does Disk in Task Manager Work?
In the context of Disk in Task Manager, a disk’s capacity is different from how much storage space you have on a disk. Specifically, Disk in Task Manager indicates how much of a disk’s read/write capability all running programs utilize.
In a Windows operating system’s Task Manager, the value of disk usage can rise up very high at times. This happens when the capacity of the computer’s disk is fully used to run programs.
You may notice that disk usage rises up to 70% or 100% when your computer boots up. At that point, your computer is opening applications that run at the computer’s startup.
Some applications that may run at a computer’s startup include Skype, antivirus programs, and so on.
Nevertheless, during normal day-to-day operation, the value of disk space usage falls to about 5% or less. If the usage of the disk in task manager remains high always, then something may be wrong with the computer.
A constant high disk usage value slows your computer down or causes a “System not responding” error. Speaking of constant high space usage, it could be that too many apps are running in the background.
Simply put, your computer will perform better if the value of disk usage in the task manager is low.
Features of Disk in Task Manager
At this point in our discussion, you should be able to differentiate a disk in task manager from a physical disk. Moreover, you can tell how this Windows Operating Systems feature works.
In this section, we’ll focus properly on the features of Disk in Task Manager.
Disk in Task Manager does not Depend on Actual Storage Capacity
As I have hinted more than once, Disk in Task Manager means how much of a disk’s capacity is currently used to perform read/write operations. Meanwhile, storage capacity is the maximum amount of data an HDD or SSD storage can store.
Therefore, the total capacity, used space, or available space on a disk is not the same as its utilization in the Task Manager.
In short, disk utilization in Task Manager can read 0% even when you have 30GB of files on your hard drive.
It is Measured as a Percentage of the Total Disk Capacity
The total usage of a disk in task manager is measured in percentage. The percentage value changes every second, just like a digital clock.
Specifically, this percentage value is expressed in relation to the disk’s average read and write speed.
By read speed, I mean the rate at which the disk opens a file or program. Also, the write speed is how fast the disk can save files.
Thus, when many programs are open and running simultaneously, the disk utilization rises significantly. For PCs with a hard disk drive, you will notice the platters spinning faster at that point.
Individual Processes on Disk are Measured in Megabytes Per Second (MB/s)
All running applications (including background processes) in the Processes tab have distinct values.
Unlike the total value of Disk utilization measured in percentage, disk usage by individual applications is measured in MB/s.
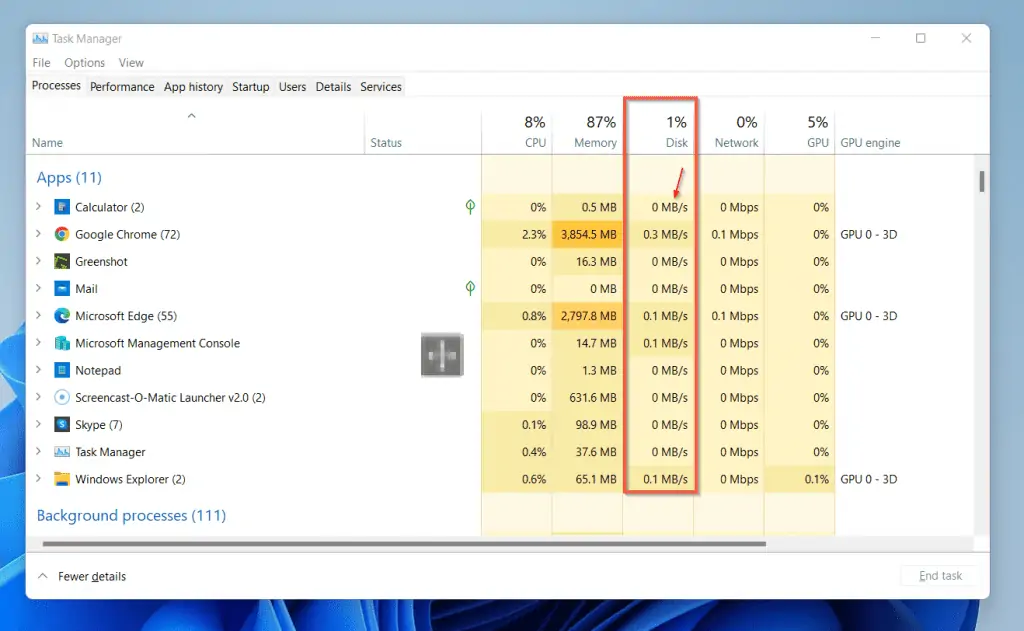
This shows the average speed at which the disk is reading the application’s program and data.
Disk Utilization Contributes to your PC’s Overall Performance
When the usage value of a disk rises very high, the computer’s performance drops significantly. In severe cases, the computer may freeze or show “Apps not responding” errors.
Normally, one may encounter this challenge when the disk usage is at or near 100%. This is quite different from the high value of disk usage you may experience after a computer startup.
Windows 11 operating system does suffer the disk usage problems at times. So, if you’re using Windows 11, one way to minimize disk usage is disallowing several apps from running in the background.
Pros of Low Disk Usage in Task Manager
Low Disk Usage Lets a Computer Perform Faster
When the level of disk usage in the task manager is between 0% and 5%, you’ll notice your computer performing faster.
It Gives Additional Information About a Disk
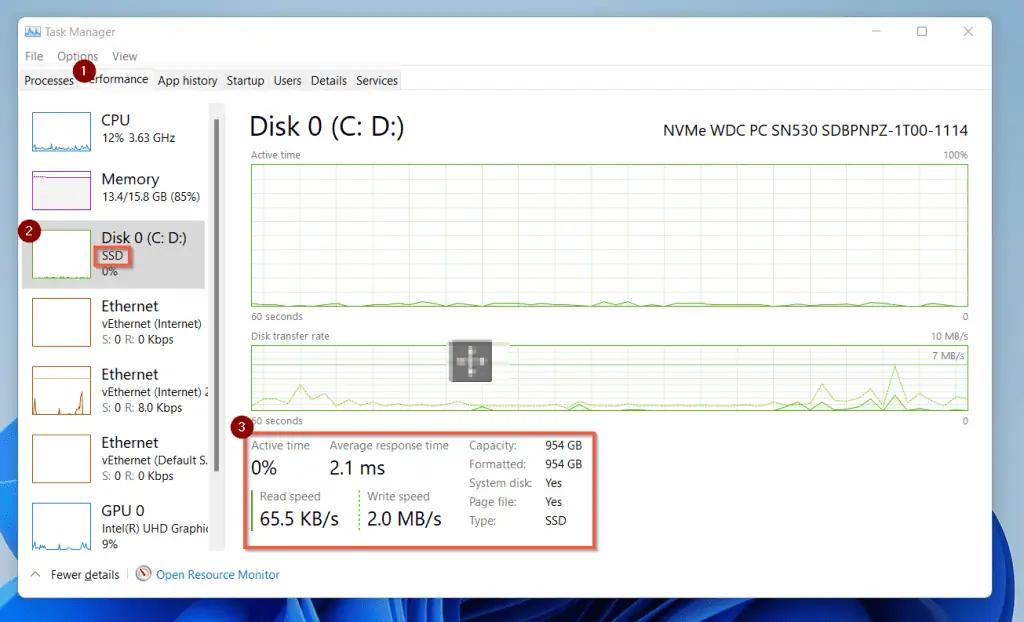
Apart from the read/write speed of a disk, the performance tab of the task manager gives additional information.
The additional information you’ll find on the Performance tab includes the type of disk (HDD or SSD) [labeled (2) in the screenshot below]. Also, you will see some other useful information like the disk’s Active time, Average response, Read speed and write speed.
Disk Usage Performance Can Be Improved
If your disk usage is too high for a long time, here are a few easy steps to reduce it.
i. Clean junk files, cached data, or temporary files. These tasks can also be performed with a tool like Ccleaner.
ii. Scan your PC with powerful antivirus software; don’t just depend on Windows defender alone.
iii. Uninstall apps that you don’t use often; you can install them when you need to use them.
iv. Perform a clean boot. A clean boot will restart Windows OS but will load only some drivers and programs, not all of them.
v. Update your Windows OS, making sure the update includes patches for fixing disk usage errors.
The Task Manager Provides Information on Background Processes
A background process is software that runs behind the scenes and is not visible to the person using a computer. Moreover, such software does not need the user to start them before it can start running.
Interestingly, the disk usage information is presented alongside that of other processes. Therefore, the task manager gives information about background processes that ordinarily are not visible to the user.
For instance, Task Manager displays processes using the CPU, RAM, and network.
Cons of High Disk Usage in Task Manager
High Disk Usage Slows a Computer Down
I mentioned earlier how significant the effect of high disk usage could be on a computer.
If the level of disk usage remains close or is at 100% long after booting, it slows the computer’s performance. Moreover, the programs you’re running may not respond sometimes.
You do not Have Control Over the Information Displayed by Disk in Task Manager
You can not customize the disk usage level by yourself. Rather, it depends on the apps’ activities in the foreground and background.
Nevertheless, you can minimize disk usage by having updated driver software and operating systems on your computer.
High Usage Value Can Affect Users’ Experience in Gaming
Heavy graphics games load slower when disk usage is high. Furthermore, the frame rate at which the game plays might stutter.
This would cause motions in games not to be smooth even when other components like the GPU are good.
High Disk Usage May Lead to Further Problems on a Computer
Other factors beyond a user’s control can increase disk usage. Such factors as computer viruses and disk faults are notable causes of high disk utilization.
If these problems are not solved on time, they may result in loss of data on the disk.
Conclusion
Disk in Task Manager is one area that many computer users pay less attention to. As you have seen in this guide, it can affect how fast or slow a PC performs.
Therefore, you shouldn’t wait until your PC quits before checking the disk usage. Once you notice an unusual lag with your PC, one troubleshooting step is to check the disk usage.
So, always clean junk files and avoid setting too many apps to run at startup. Also, uninstall unnecessary and old apps.
You can install them later when you need them.
Paying attention to your PC’s disk usage level may save you the troubles of an unresponsive PC.
I hope I was able to explain Disk in Task Manager and how it works. I also hope that you found the article easy to understand.
If you found the article helpful and easy to understand, click on “Yes” beside the “Was this page helpful” question below. You may also express your thoughts and opinions by using the “Leave a Comment” form at the bottom of this page.
Finally, you may find other helpful articles on our Storage & Disk Technology Explained page.